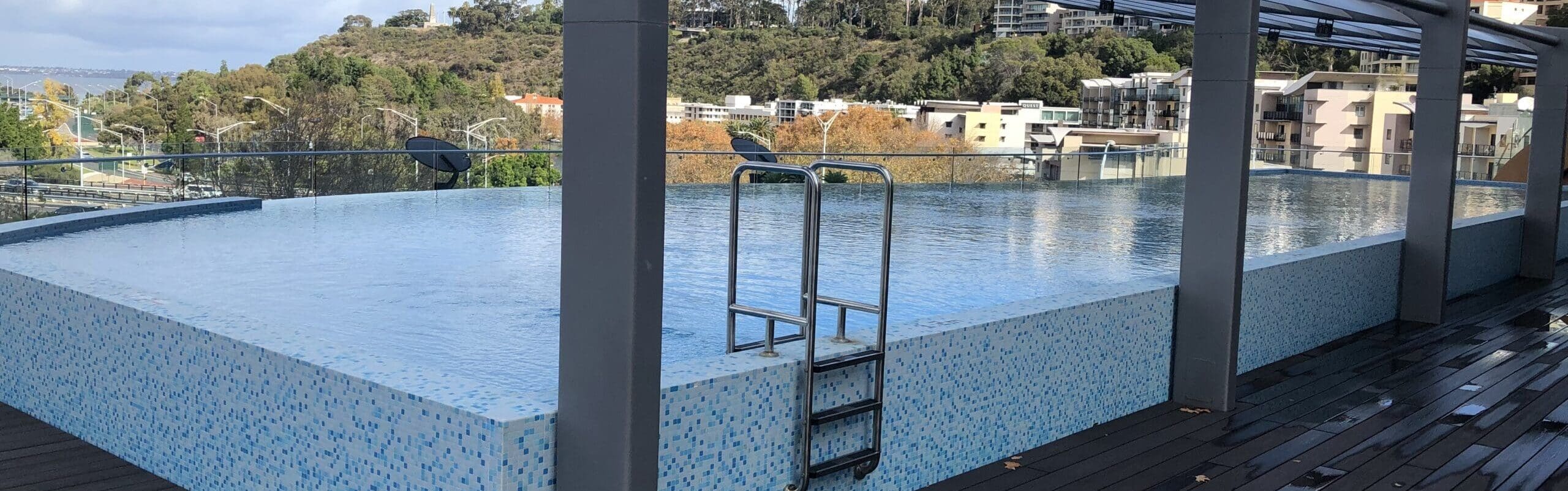

Rooftop swimming pool heating in Perth, WA
Bowman and Rinnai provide the perfect heating solution for an Australian roof top pool – where winter temperatures can be surprisingly cool!
Used to cool the hot, compressed air from the turbo before it reaches the engine, the intercoolers improve engine efficiency and reduce emissions for marine and land-based stationary engines.

Exhaust gas heat exchangers are designed to recover waste heat energy from the exhaust stream of reciprocating engine powered generating sets.

Bowman 'copper free' fuel coolers are compact, highly efficient heat exchangers suitable for fuel conditioning rigs in the automotive testing industry.
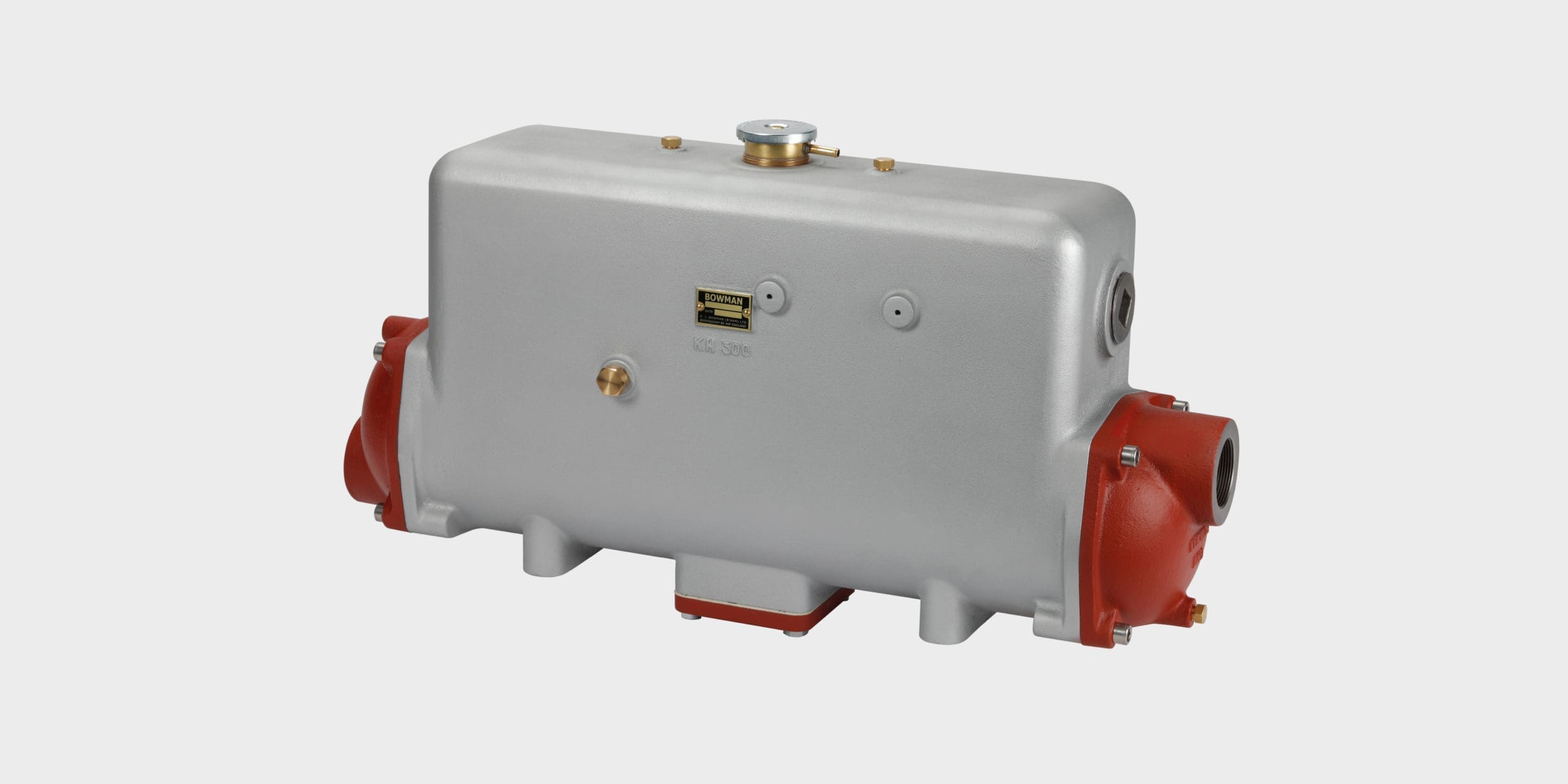

Engine coolant header tank heat exchangers for marine propulsion, gensets or stationary land-based engines.
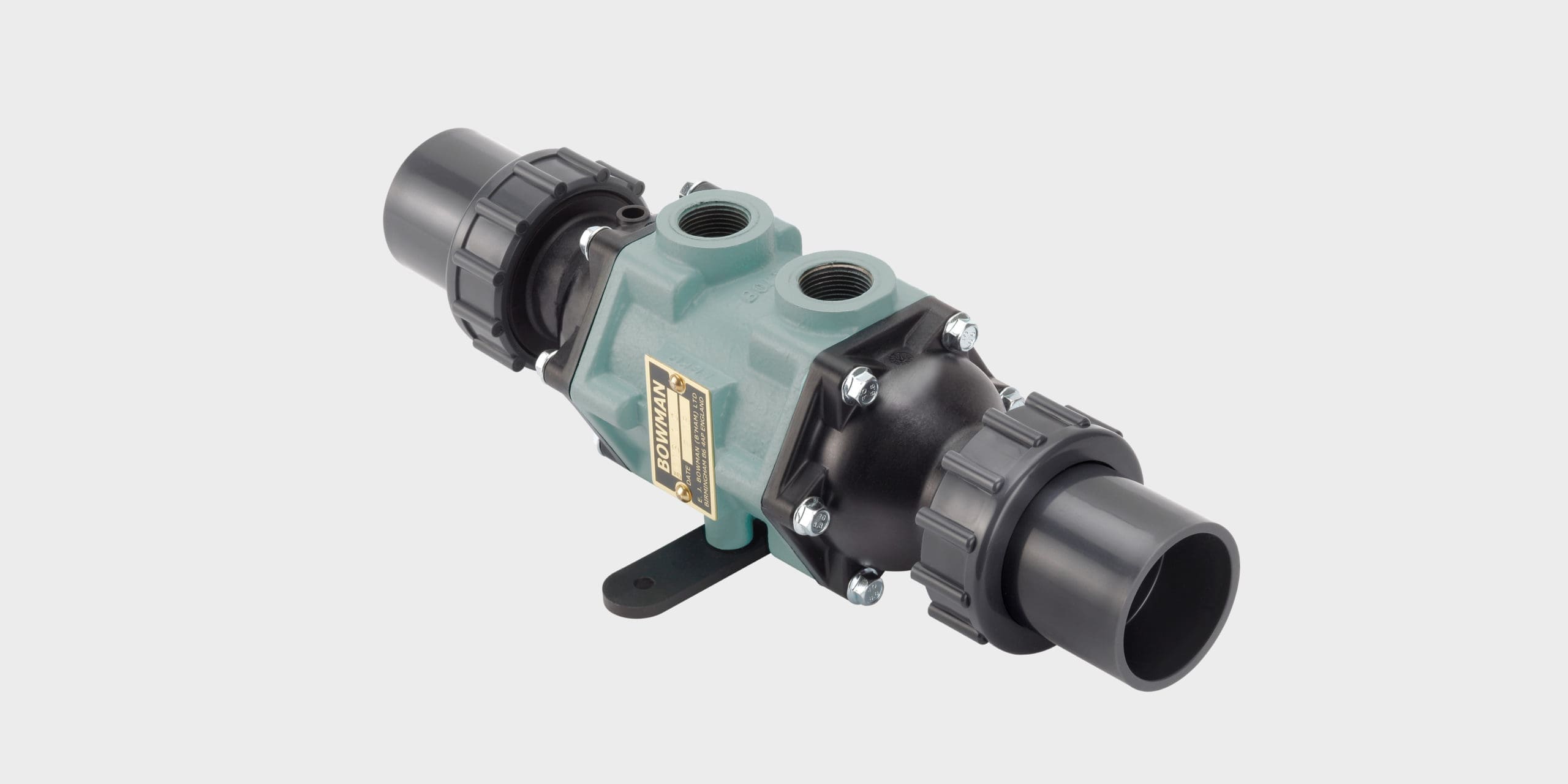

Bowman EC 80-5113-1T heat exchangers provide a new solution for heating spas and hot tubs in just a fraction of the time taken by traditional electric heaters.
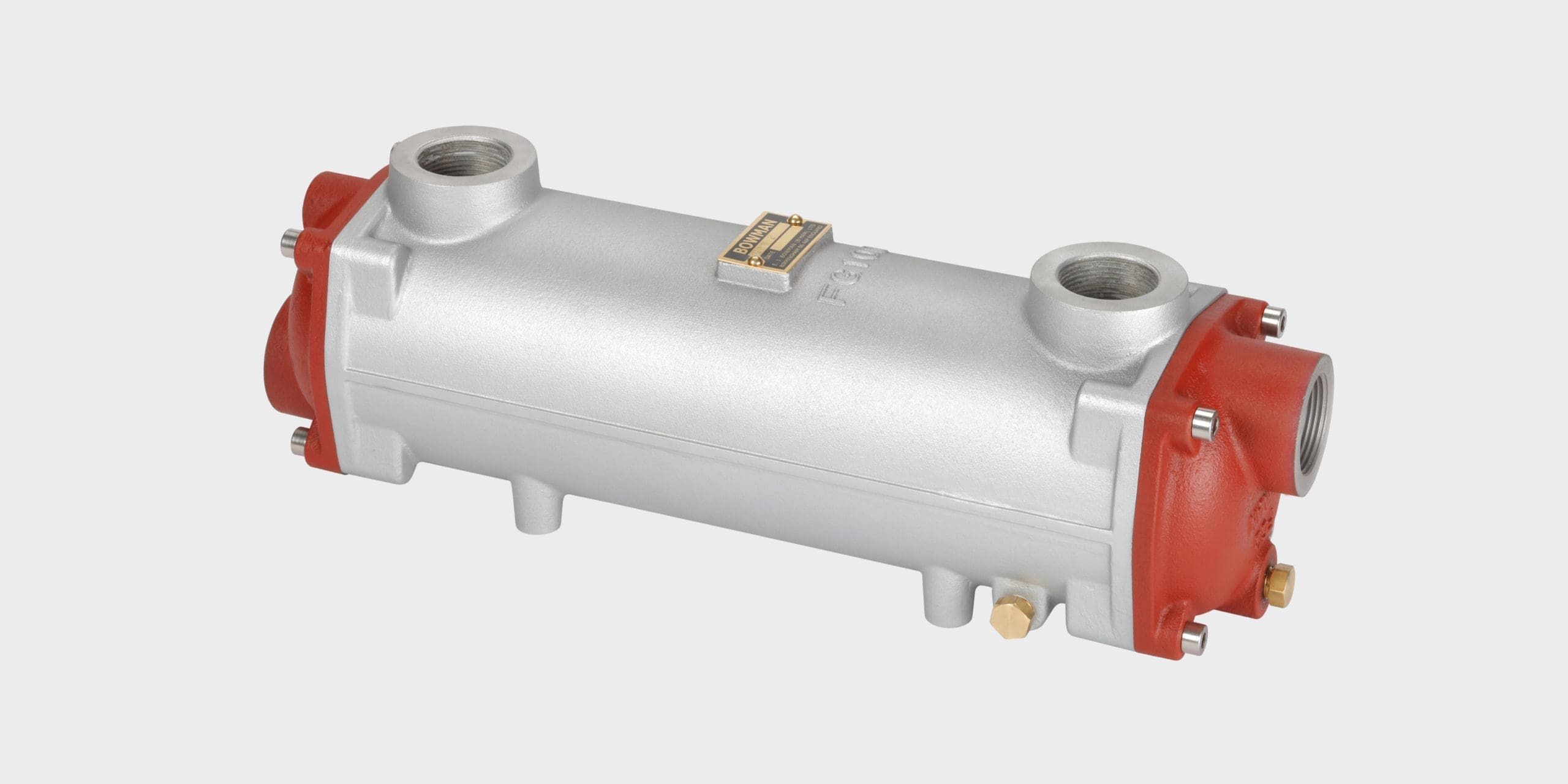

Highly efficient heat transfer solutions for cooling marine, land-based and underground hydraulic systems.

Bowman inline plate heat exchangers are a compact, economical solution for high efficiency heat transfer.

Bespoke cooling solutions for a range of popular marine engines from major OEMs, including coolant heat exchangers, charge air coolers, plus combined heat exchangers and exhaust manifolds, suitable for cooling marine engines up to 1 MW.
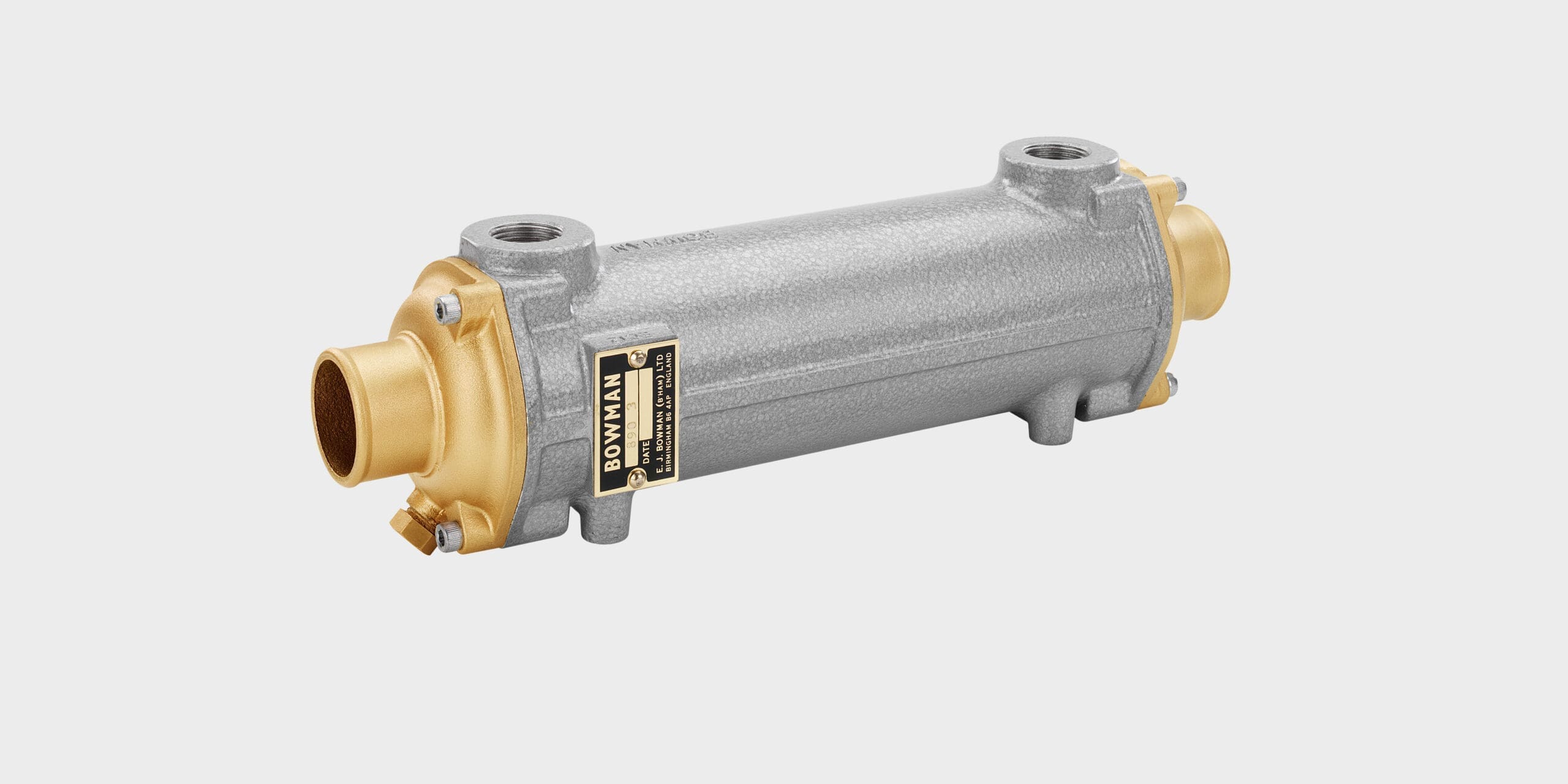

Bowman has a range of highly efficient oil coolers designed for marine and industrial engines and transmissions.

Efficient heat exchangers for cooling electric marine motors, hydrogen fuel cells, battery packs, chargers, AC-DC converters, DC-DC converters, inverters and associated equipment for electric and hybrid marine propulsion and charging systems.

Highly efficient heat transfer solutions for cooling a variety of applications where air and fluids need to be cooled by fluids.

Many applications require stainless steel shell and tube heat exchangers and Bowman provide a standard range of units that are suitable for cooling or heating a variety of fluids.

Bowman swimming pool heat exchangers are renowned for reliability and efficiency. Whether heating your pool with a traditional boiler or a renewable energy source, Bowman is the obvious choice.

Premium quality heat exchangers and oil coolers for precise temperature control of engines under test cell development conditions.

Recovering waste heat energy from engine powered generating sets for biogas, diesel and natural gas applications up to 1 MW.

Efficient cooling for stationary / land-based engines where air cooling is either unavailable or inappropriate.

The reliable solution for cooling Electric & Hybrid Marine Propulsion Systems.

A comprehensive oil cooling solution for industrial hydraulic control systems, plus high temperature and mining applications.

A complete solution for cooling complex on-board hydraulic equipment, including thruster and stabiliser systems.

The complete cooling solution for marine engine propulsion, including the latest electric and hybrid systems.
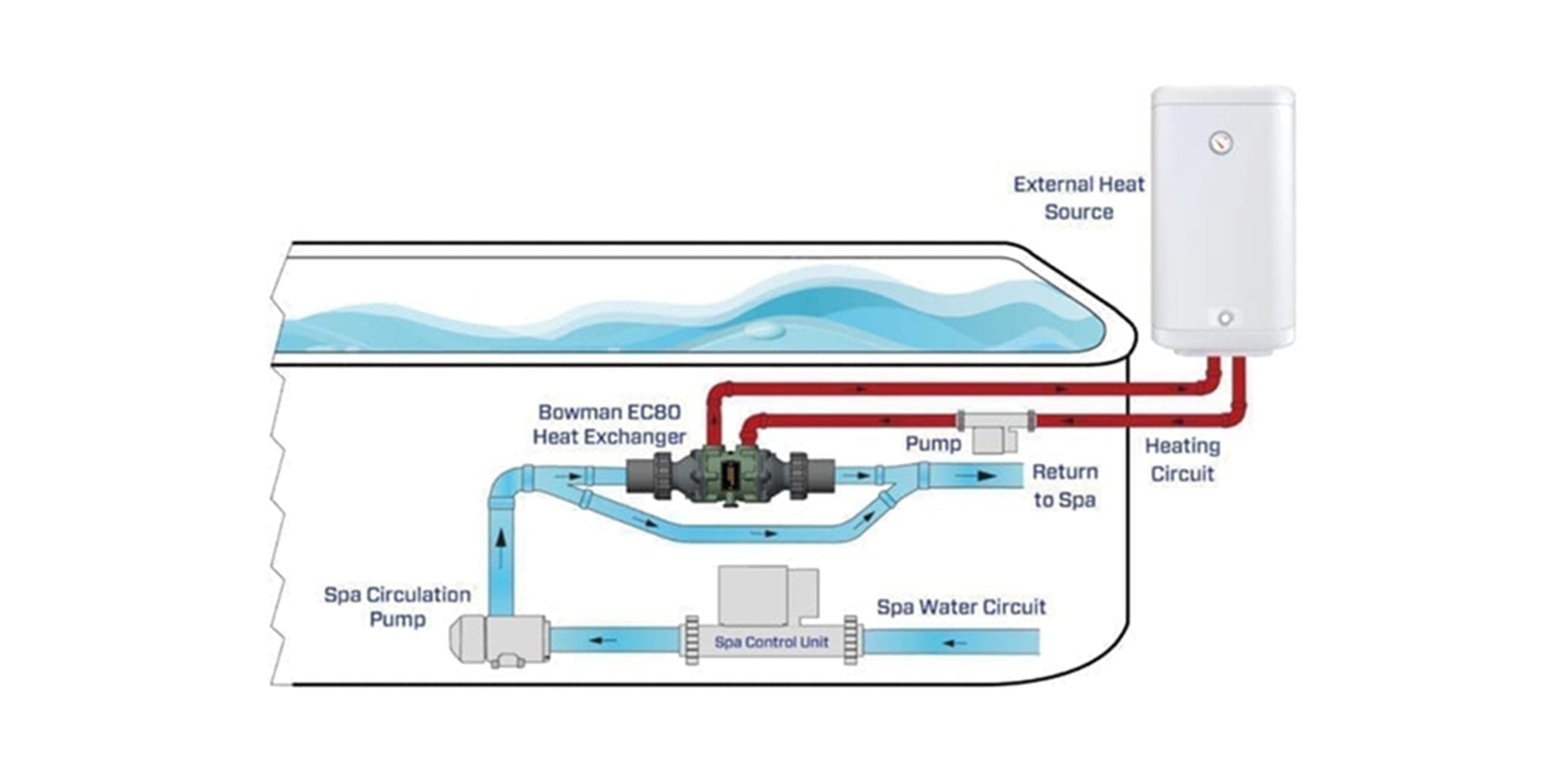
An energy efficient solution for heating hot tubs and swim spas faster, significantly reducing heat-up time for guest change-over periods.

Quality heat exchangers for efficient swimming pool heating, using boiler or renewable energy heat sources.
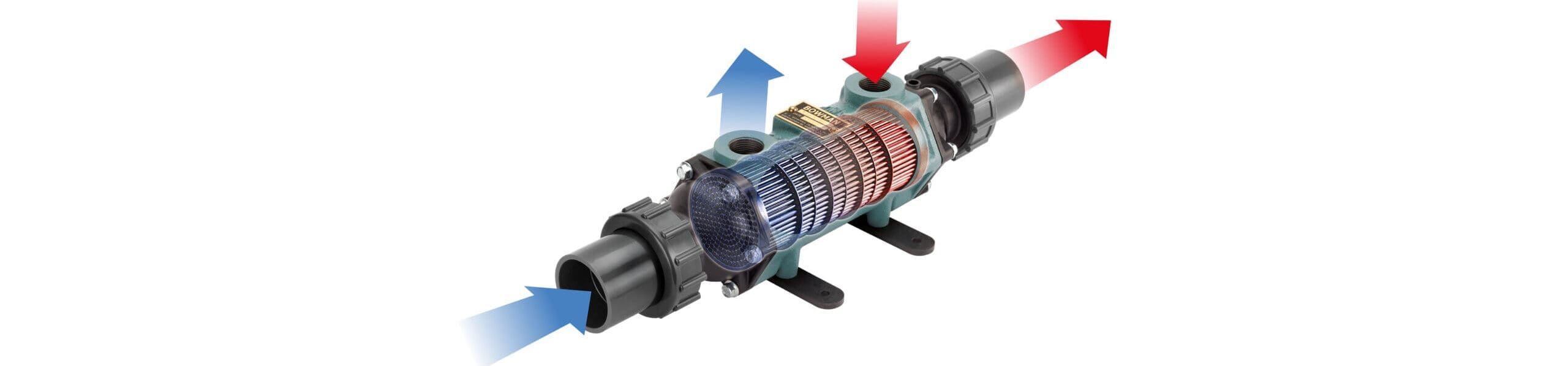
Swimming pool heat exchangers are devices that will ensure that your pool water is always at the desired temperature without having to use electricity to heat it up. Instead, they move thermal energy from a heat source such as a gas or boiler, solar thermal system, or heat pump into the pool water. Such an approach not only helps conserve energy but also provides a reliable and economical way of providing warm water for an extended swimming season, even in the coldest of climates. Bowman have become industry leaders in the manufacture of efficient, corrosion-resistant heat exchangers suitable for residential and commercial pools.
At the heart of every pool heat exchanger is the principle of thermal transfer. Essentially, heat exchangers move heat from one fluid to another without the two mixing. In a typical pool set-up, hot water from a boiler, or other heat source, flows through one side of the exchanger, while cooler pool water flows through the other. The heat passes through the exchanger’s walls, warming the pool water as it circulates back into the pool. The greater the temperature difference between the two fluids, the more efficiently heat is transferred.
In addition, the rate at which both fluids flow through the exchanger plays a crucial role in determining how quickly and effectively the pool water heats up.
A swimming pool heat exchanger consists of several key components. The two main circuits are the ‘primary’ circuit, which brings in hot water from the heat source, and the ‘secondary’ pool water circuit, which carries the pool water that needs heating. Inside the exchanger, these circuits are separated by metal surfaces – either tubes or plates – made from materials like stainless steel, copper-nickel or titanium to resist corrosion from pool chemicals. Some designs, such as the shell-and-tube type, feature a bundle of tubes enclosed in a cylindrical shell, while plate heat exchangers use a stack of thin, corrugated plates to maximise surface area. Temperature sensors and flow control valves are often included to monitor and regulate the process.
The heat exchange process begins when the heat source, such as a boiler, heats water and pumps it into the exchanger’s primary circuit. Simultaneously, the pool pump circulates cooler pool water through the exchanger’s pool water circuit. As the two fluids pass through their respective channels, the hot boiler water transfers its heat through the exchanger’s walls to the cooler pool water. This process continues in a loop: the now-warmed pool water returns to the pool, while the cooled boiler water is sent back to the heat source to be reheated. Automated controls can adjust the flow rates and temperatures to achieve and maintain the ideal pool temperature.
There are two main types of heat exchangers used in swimming pools: shell-and-tube and plate heat exchangers. Shell-and-tube models are particularly popular for all types of residential and commercial pools because they offer a large surface area for heat transfer, they can accept high flow rates making them easy and cheaper to install, and maintenance is simple especially when designed with a floating tube stack. Plate heat exchangers are efficient but can be more expensive. They normally require additional pipework to bypass the heat exchanger to avoid excessive pressure drop making them more difficult to install and maintenance is difficult, or virtually impossible.
There are quite a number of advantages of using a heat exchanger to warm your pool. First of all, they are very energy-efficient since they can use existing heat sources instead of producing heat from electricity. This not only cuts your energy bills but also the impact you have on the environment. The heat exchangers are durable, especially when made from high-quality materials, and they will help to safeguard your boiler against corrosive pool chemicals. Also, these systems can be expanded to match pools of all sizes ranging from small home spas to Olympic size installations.
To keep your swimming pool heat exchanger running smoothly, regular maintenance is essential. From time to time, examine the unit for presence of leaks, corrosion or scaling and make sure that the pool water circuits’ flow rate is within the range recommended by the manufacturer. Balanced pool water chemistry is important because imbalanced water can speed up corrosion or scaling. In the colder climates, remember to remove the heat exchanger before winter to avoid frost damage.
Finally, optimising the temperature differential between the heat source and pool water will help your system heat the pool quickly.
Swimming pool heat exchangers provide a reliable, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly solution for pool heating. By understanding how these systems work, their components, and the importance of proper maintenance, pool owners can enjoy warm, inviting water all season long, without the high costs or environmental impact of electric heating.
Swimming pool heat exchangers are devices that will ensure that your pool water is always at the desired temperature without having to use electricity to heat it up. Instead, they move thermal energy from a heat source such as a gas or boiler, solar thermal system, or heat pump into the pool water. Such an approach not only helps conserve energy but also provides a reliable and economical way of providing warm water for an extended swimming season, even in the coldest of climates. Bowman have become industry leaders in the manufacture of efficient, corrosion-resistant heat exchangers suitable for residential and commercial pools.
At the heart of every pool heat exchanger is the principle of thermal transfer. Essentially, heat exchangers move heat from one fluid to another without the two mixing. In a typical pool set-up, hot water from a boiler, or other heat source, flows through one side of the exchanger, while cooler pool water flows through the other. The heat passes through the exchanger’s walls, warming the pool water as it circulates back into the pool. The greater the temperature difference between the two fluids, the more efficiently heat is transferred.
In addition, the rate at which both fluids flow through the exchanger plays a crucial role in determining how quickly and effectively the pool water heats up.
A swimming pool heat exchanger consists of several key components. The two main circuits are the ‘primary’ circuit, which brings in hot water from the heat source, and the ‘secondary’ pool water circuit, which carries the pool water that needs heating. Inside the exchanger, these circuits are separated by metal surfaces – either tubes or plates – made from materials like stainless steel, copper-nickel or titanium to resist corrosion from pool chemicals. Some designs, such as the shell-and-tube type, feature a bundle of tubes enclosed in a cylindrical shell, while plate heat exchangers use a stack of thin, corrugated plates to maximise surface area. Temperature sensors and flow control valves are often included to monitor and regulate the process.
The heat exchange process begins when the heat source, such as a boiler, heats water and pumps it into the exchanger’s primary circuit. Simultaneously, the pool pump circulates cooler pool water through the exchanger’s pool water circuit. As the two fluids pass through their respective channels, the hot boiler water transfers its heat through the exchanger’s walls to the cooler pool water. This process continues in a loop: the now-warmed pool water returns to the pool, while the cooled boiler water is sent back to the heat source to be reheated. Automated controls can adjust the flow rates and temperatures to achieve and maintain the ideal pool temperature.
There are two main types of heat exchangers used in swimming pools: shell-and-tube and plate heat exchangers. Shell-and-tube models are particularly popular for all types of residential and commercial pools because they offer a large surface area for heat transfer, they can accept high flow rates making them easy and cheaper to install, and maintenance is simple especially when designed with a floating tube stack. Plate heat exchangers are efficient but can be more expensive. They normally require additional pipework to bypass the heat exchanger to avoid excessive pressure drop making them more difficult to install and maintenance is difficult, or virtually impossible.
There are quite a number of advantages of using a heat exchanger to warm your pool. First of all, they are very energy-efficient since they can use existing heat sources instead of producing heat from electricity. This not only cuts your energy bills but also the impact you have on the environment. The heat exchangers are durable, especially when made from high-quality materials, and they will help to safeguard your boiler against corrosive pool chemicals. Also, these systems can be expanded to match pools of all sizes ranging from small home spas to Olympic size installations.
To keep your swimming pool heat exchanger running smoothly, regular maintenance is essential. From time to time, examine the unit for presence of leaks, corrosion or scaling and make sure that the pool water circuits’ flow rate is within the range recommended by the manufacturer. Balanced pool water chemistry is important because imbalanced water can speed up corrosion or scaling. In the colder climates, remember to remove the heat exchanger before winter to avoid frost damage.
Finally, optimising the temperature differential between the heat source and pool water will help your system heat the pool quickly.
Swimming pool heat exchangers provide a reliable, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly solution for pool heating. By understanding how these systems work, their components, and the importance of proper maintenance, pool owners can enjoy warm, inviting water all season long, without the high costs or environmental impact of electric heating.

Bowman and Rinnai provide the perfect heating solution for an Australian roof top pool – where winter temperatures can be surprisingly cool!

Six Bowman heat exchangers have been installed at the recently opened Gold’s Gym, Amman, Jordan, to heat two half Olympic-sized swimming pools.

How Bowman heat exchangers are helping this internationally renowned golf destination reduce energy costs and CO₂ emissions.

Bowman heat exchangers are playing an important role in the success of a flagship hotel on the Black Sea coast in Georgia.

Bowman and Rinnai provide the perfect heating solution for an Australian roof top pool – where winter temperatures can be surprisingly cool!

Six Bowman heat exchangers have been installed at the recently opened Gold’s Gym, Amman, Jordan, to heat two half Olympic-sized swimming pools.

How Bowman heat exchangers are helping this internationally renowned golf destination reduce energy costs and CO₂ emissions.

Bowman heat exchangers are playing an important role in the success of a flagship hotel on the Black Sea coast in Georgia.